Introduction:
AI-generated voicemail is now widely used in B2B sales for follow-ups, reminders, and outbound outreach. But as of 2026, its legality depends entirely on how it is delivered, who receives it, and whether proper consent exists under the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA).
In the eyes of U.S. regulators, AI-generated voicemail is treated the same as any artificial or prerecorded voice. This means businesses cannot assume that using AI, ringless voicemail, or automated delivery methods reduces compliance obligations. In many cases, it increases legal exposure.
This guide explains whether AI voicemail is legal in 2026, how TCPA rules apply specifically to B2B sales teams, and what steps companies must take to stay compliant while using AI-driven voicemail at scale.
What Is AI Voicemail?
AI voicemail refers to voicemail messages that are generated, delivered, or triggered using artificial intelligence systems rather than a human speaking live. These messages may be created using text-to-speech, voice cloning, or automated workflows and are commonly used for outbound sales, reminders, and follow-ups.
From a legal perspective, AI voicemail is classified as an artificial or prerecorded voice under the TCPA. This classification applies regardless of whether the voicemail is delivered through a traditional call, automated dialing system, or ringless voicemail technology.
As of 2026, U.S. regulators including the Federal Communications Commission make no distinction between human-recorded and AI-generated voicemail when enforcing TCPA consent requirements. The determining factor is how the message is delivered and whether valid consent exists, not how the voice was created.
How Do TCPA Rules Apply to AI-Generated Voicemail in 2026?
In 2026, AI-generated voicemail is treated the same as robocalls under the TCPA if it uses automation or a prerecorded voice.
How Regulators Interpret AI Voicemail
TCPA enforcement focuses on automation, not novelty. If an AI system sends a voicemail without a human dialing and speaking in real time, it is classified as an automated or prerecorded message.
Key TCPA Triggers for AI Voicemail
Uses a prerecorded or synthetic voice
Initiated automatically by software or AI
Delivered to a consumer’s mobile phone
Sent for sales, marketing, or promotional purposes
Outcome: AI voicemail falls under TCPA robocall rules, regardless of how “human” it sounds.
What Type of Consent Is Required for Legal AI Voicemail?
Most AI voicemails require prior express consent. Marketing-related messages often require prior express written consent.
Consent Requirements Explained
TCPA consent must be explicit and verifiable. It must be tied directly to the phone number contacted and the purpose of the message.
Valid Consent Must Be?
Explicitly granted by the recipient
Specific to automated or prerecorded messages
Linked to the exact phone number used
Stored and auditable
What Does NOT Count as Consent?
Business cards or email signatures
Scraped or purchased phone lists
Prior email conversations
Implied or assumed permission
Risk Without Consent: AI voicemail sent without proper consent exposes companies to statutory penalties, class-action lawsuits, and enforcement action.
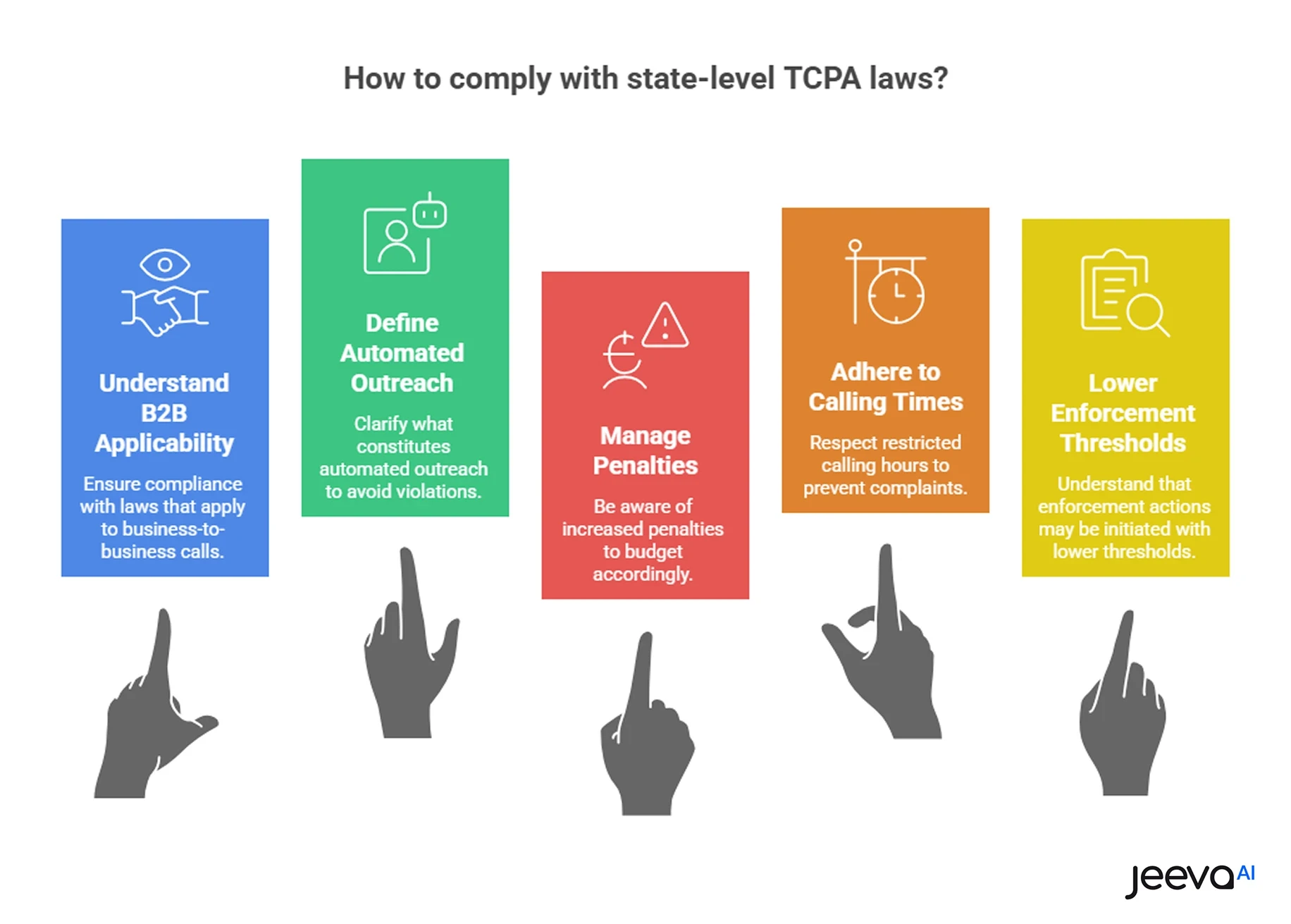
Federal vs State TCPA Laws: What B2B Teams Must Know
B2B teams must comply with both federal TCPA rules and stricter state-level “mini-TCPA” laws. State laws can apply even when federal TCPA allows outreach.
How Federal and State TCPA Laws Differ
The federal TCPA sets a baseline for automated calls, prerecorded messages, and consent requirements. However, many U.S. states have enacted their own laws that go further especially around automation and voicemail drops.
State-level TCPA laws often:
Apply to B2B calls, not just consumers
Expand what qualifies as automated outreach
Increase statutory penalties per violation
Restrict calling times more narrowly
Lower thresholds for enforcement actions
Because AI voicemail relies on automation, it frequently triggers both federal and state scrutiny.
Why State Laws Create Higher Risk for B2B Teams
AI voicemail compliance depends on the recipient’s location, not the sender’s. This means a single outbound campaign may be subject to multiple state laws simultaneously.
Common high-risk states include:
California (CCPA + mini-TCPA overlap)
Florida (FTSA with strict automation rules)
Washington
Oklahoma
Pennsylvania
Ignoring state-specific rules is one of the most common causes of TCPA violations in AI-driven outreach.
What B2B Teams Must Do to Stay Compliant
To reduce risk, B2B teams using AI voicemail should:
Apply location-based dialing and voicemail rules
Maintain state-aware consent logic
Suppress numbers in restricted jurisdictions
Log consent and outreach activity for audits
Use compliance-aware AI systems
Federal TCPA compliance is not enough: B2B teams deploying AI voicemail must account for state-level TCPA laws, which often impose stricter limits even on business outreach.
AI-driven calling without state-aware compliance controls significantly increases legal and financial risk.
State-by-State TCPA Risk Callouts (High-Risk States)
Some U.S. states enforce stricter TCPA-style laws that significantly increase risk for AI voicemail even in B2B outreach.
Florida (FTSA): Florida’s Telephone Solicitation Act is one of the most aggressive “mini-TCPA” laws. It tightly restricts automated and prerecorded voicemail, applies to B2B calls, and carries high statutory penalties. Litigation risk is especially elevated, and consent standards are narrow.
California: California layers strong privacy and consumer protection laws on top of TCPA enforcement. AI-generated voicemail faces heightened scrutiny, particularly when there is marketing or promotional intent, even in commercial outreach.
Washington: Washington requires enhanced consent, disclosure, and identification for automated calls and voicemail drops. B2B exemptions are limited, making AI voicemail risky without explicit, well-documented consent.
Texas: Texas enforces its own telemarketing statutes with meaningful penalties. Automated or prerecorded voice messages can trigger liability in both consumer and business contexts if compliance controls are weak.
Risk Takeaway
If AI voicemail reaches contacts in Florida, California, Washington, or Texas, teams must apply state-specific compliance controls, stricter consent validation, and automated suppression logic. These states represent the highest TCPA risk zones for AI-driven voicemail campaigns.
Are There Exceptions for Informational or Non-Marketing Voicemails?
Yes, but they are narrow and risky.
Informational voicemails such as appointment reminders, service updates, or transactional notices may qualify for TCPA exemptions only if they contain no marketing or promotional intent. Regulators focus on the content, not the label.
If an AI voicemail includes sales language, value propositions, calls to action, or lead-generation intent, it is treated as marketing, and TCPA consent rules apply. Even subtle promotion can invalidate the exemption.
Practical takeaway: AI voicemail used in sales or outbound prospecting is rarely considered purely informational. B2B teams should assume marketing rules apply unless the message is strictly transactional, clearly documented, and consent-safe.
What Are the Penalties for TCPA Violations Using AI Voicemail?
TCPA penalties scale fast and become severe with AI. TCPA violations are charged per call or voicemail, not per campaign. If an AI system sends an unlawful voicemail, each message counts as a separate violation.
TCPA Penalty Structure
$500 per violation for standard non-compliance
Up to $1,500 per violation for willful or knowing violations
No cap on total damages in large-scale campaigns
Why AI Voicemail Increases Risk
AI systems operate at scale. A single misconfigured voicemail campaign can trigger hundreds or thousands of violations in minutes, multiplying liability instantly. Courts do not reduce penalties because the calls were automated automation increases exposure.
Real-World Risk
1,000 AI voicemails → $500,000 to $1.5M in potential liability
Class actions amplify risk through aggregated claims and legal fees
Key takeaway: AI voicemail must be deployed with strict consent controls, state-level rules, and suppression logic. Without compliance-first design, TCPA penalties can quickly outweigh any outbound ROI.
How Can B2B Teams Build a TCPA-Compliant AI Voicemail Workflow?
TCPA compliance must be engineered into the workflow not added afterward.
A compliant AI voicemail system is designed to prevent unlawful calls before they happen, not to justify them later. This requires technical controls, clear policies, and continuous monitoring.
Core Requirements for a TCPA-Compliant Workflow
1. Consent Verification (Pre-Send)
Confirm prior express (or written) consent before any voicemail is triggered
Tie consent explicitly to the phone number being contacted
Block sends when consent is missing, expired, or ambiguous
2. Geographic & State-Level Filtering
Detect recipient state in real time
Apply stricter rules for high-risk states (e.g., Florida, California, Washington, Texas)
Automatically suppress outreach where state “mini-TCPA” laws prohibit AI voicemail
3. Message Classification
Classify voicemails as marketing vs informational before delivery
Block AI voicemails containing CTAs, promotions, or sales language without proper consent
Treat most outbound sales voicemails as marketing by default
4. Human-Defined Policy Controls
Humans set consent rules, state logic, and escalation thresholds
AI executes only within those predefined guardrails
Uncertain cases are routed for manual review
5. Audit Logs & Proof of Compliance
Log consent source, timestamp, phone number, message type, and delivery outcome
Maintain records to demonstrate compliance during audits or disputes
Enable rapid suppression if opt-out or complaints occur
Governance Best Practice
AI should automate execution, not compliance decisions. Legal and RevOps teams must define the rules; AI enforces them consistently at scale.
Key takeaway: A TCPA-compliant AI voicemail workflow is built on consent verification, state-aware filtering, strict message controls, and auditable execution. When compliance is embedded at the system level, B2B teams can scale safely without regulatory risk.
TCPA-Safe AI Voicemail Examples
Example of a Lower-Risk (Still Requires Consent)
“Hi, this is Alex calling regarding the demo you requested. If now isn’t a good time, you can return the call or reply to the email we sent earlier.”
Why it’s safer:
References a prior request
No promotional claims
No urgency or CTA pressure
Example of a High-Risk (Likely Non-Compliant)
“Hi, we help companies increase revenue by 40%. Call us back today to unlock a limited offer.”
Why it’s risky:
Promotional language
No consent reference
Automated delivery implied
AI Voicemail TCPA Compliance Checklist
Compliance Area | Requirement | Status to Verify |
|---|---|---|
Consent | Prior express (or written) consent obtained | ☐ |
Message Type | Marketing vs informational clearly defined | ☐ |
Automation | Human initiation vs AI-initiated confirmed | ☐ |
State Laws | Recipient state compliance verified | ☐ |
Disclosure | Caller identity clearly stated | ☐ |
Opt-Out | Clear opt-out mechanism available | ☐ |
Record keeping | Consent and delivery logs stored | ☐ |
Volume Control | Rate limits and safeguards enabled | ☐ |
Ringless Voicemail vs. TCPA: Myth-Busting
In 2022, the FCC ruled explicitly that "ringless voicemail" dropping messages directly into voicemail inboxes without ringing the recipient’s phone is still considered a "call" under the TCPA. As a result, this method also mandates documented PEWC.
Misunderstanding or ignoring this ruling has led to a dramatic surge in litigation:
TCPA class actions jumped 112% YoY in Q1 2025, with 80% seeking class certification.
Significant penalties include a $6 million fine for an AI-generated political robocall and a $1 million settlement by a carrier involved in such calls.

Understanding Consent: How to Obtain Opt-In Consent at Scale
To legally deploy AI voicemails in your cold outreach campaigns, obtaining robust consent is essential:
Prior Express Written Consent (PEWC): Mandatory for all AI-driven sales voicemails to wireless numbers. Consent must explicitly acknowledge agreement to receive artificial voice messages and be brand-specific.
Established Business Relationship (EBR): Valid only for informational messages, such as onboarding or transactional updates not cold sales.
Capture valid consent effectively through:
Web form checkboxes with IP logging.
Double opt-in SMS verification.
Secure electronic signatures.
State-Level Landmines for B2B Sellers
Federal rules aren't your only concern. Several states have enacted their own "mini-TCPA" regulations:
Florida (FTSA): Despite 2023 amendments narrowing the autodialer definition, the law still aggressively targets unsolicited B2B calls. Violations carry fines of $500-$1,500 per violation.
Oklahoma, Maryland, Washington: Similar state-level TCPA regulations impose tighter opt-out and call-time rules.
California (CCPA/CPRA): Requires disclosure when AI-driven automated decision-making involves personal data.

Your Compliance Checklist for AI Voicemail Outreach
Implementing a compliance-first approach is crucial for B2B firms leveraging AI voicemail:
Consent Vault: Document and store consent records meticulously (timestamps, consent language, IP address).
Geo-aware Dialing Rules: Automatically restrict voicemails to states requiring explicit opt-ins unless consent is confirmed.
Dynamic Disclosures: Clearly state brand identity, callback details, and provide easy opt-out instructions.
Do-Not-Call (DNC) Hygiene: Regularly update outreach lists against national and state DNC registries.
STIR/SHAKEN Compliance: Partner with verified telecom carriers to authenticate your calls and avoid call-blocking or spoofing accusations.
How Jeeva AI Simplifies Compliance
Jeeva AI, an agentic AI platform, prioritizes regulatory compliance to ensure seamless, risk-free outreach:
TCPA Guardian Module: Automatically manages consent records, blocks non-compliant calls, and provides a centralized audit trail.
Consent-Aware AI Messaging: Intelligent scripts that dynamically integrate mandated legal disclosures and adjust compliance based on jurisdiction.
Audit-Ready Documentation: Immutable logs tracking consent, call details, and voicemail content for audit trails and dispute resolutions.
Strategic Advantages of Compliance-first AI Outreach
Leading your market positioning with compliance offers distinct advantages:
Reduces risk of expensive class-action litigation and reputational damage.
Builds customer trust through transparency and ethical marketing practices.
Positions your business ahead of competitors who overlook regulatory diligence.
Conclusion
AI voicemail can enhance sales outreach efficiency, but it carries substantial legal risk when deployed without proper safeguards. In 2025, TCPA enforcement continues to treat automated voicemail as a regulated communication channel, especially when AI systems initiate delivery.
B2B teams must design compliance into their workflows, account for state-level laws, and treat consent as a foundational requirement. When implemented responsibly, AI voicemail can support sales operations without exposing organizations to unnecessary legal exposure.





